Getting started with MAUI
This tutorial series is designed to demonstrate how to create a .NET Multi-platform App UI (.NET MAUI) app that only uses cross-platform code. That is, the code you write won’t be specific to Windows, Android, iOS, or macOS. The app you’ll create will be a note-taking app, where the user can create, save, and load multiple notes.
In this tutorial, you learn how to:
- Create a .NET MAUI Shell app.
- Run your app on your chosen platform.
- Define the user interface with eXtensible Application Markup Language (XAML), and interact with XAML elements through code.
- Create views and bind them to data.
- Use navigation to move to and from pages.
The content of the tutorial is heavily based on the standard Microsoft tutorial which uses Visual Studio IDE as the development tool. This version has been modified to use Visual Studio Code (VSCode) but the result should be the same. In the first stage, your app will allow users to enter a note and save it to device storage.
1. Create a project
Copy and clone the stub repo into your project workspaces folder.
Open the new project in VSCode and delete the existing Haulage project folder and the solution file Haulage.sln.
Commit the changes and provide a suitable commit comment when prompted.
Create a new project with the .NET: New project… option on the VSCode command palette. When prompted for a template, select .NET MAUI App and call it Notes.
Edit the file .gitignore replacing all references to Haulage with Notes.
Commit these changes as well.
This essentially re-creates the original dummy project with a different name.
2. Customise the app shell
When VSCode creates a .NET MAUI project four important code files are generated. These can be seen in the Solution Explorer pane:
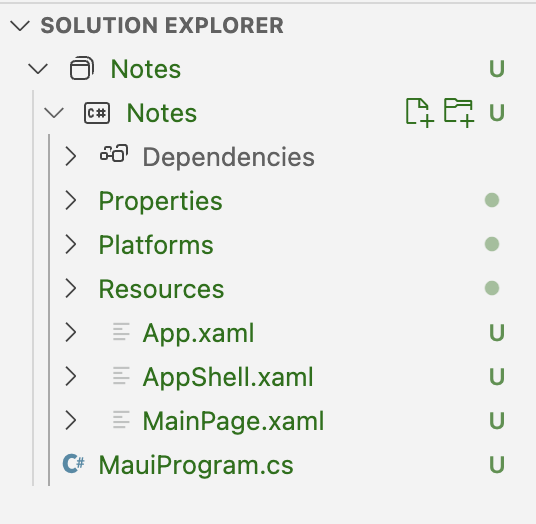
These files help get the .NET MAUI app configured and running. Each file serves a different purpose as described below:
MauiProgram.cs
This is a code file that bootstraps your app. The code in this file serves as
the cross-platform entry point of the app, which configures and starts the app.
The template startup code points to the App class defined by the App.xaml file.
App.xaml and _App.xaml.cs
Just to keep things simple, both of these files are referred to as a single file. There are generally two files with any XAML file, the .xaml file itself, and a corresponding code file that is a child item of it in the Solution Explorer. The .xaml file contains XAML markup and the code file contains code created by the user to interact with the XAML markup.
The App.xaml file contains app-wide XAML resources, such as colours, styles,
or templates. The App.xaml.cs file generally contains code that instantiates
the Shell application. In this project, it points to the AppShell class.
AppShell.xaml and _AppShell.xaml.cs
This file defines the AppShell class, which is used to define visual hierarchy
of the app.
MainPage.xaml and _MainPage.xaml.cs
This is the startup page displayed by the app. The MainPage.xaml file defines the UI (user interface) of the page. MainPage.xaml.cs contains the code-behind for the XAML, like code for a button click event.
Add an “About” page
The first customization you’ll do is add another page to the project. This page is an “about” page, which represents information about this app, such as the author, version, and perhaps a link for more information.
- In the Solution Explorer pane of VSCode, right-click the Notes project and select Add New File…
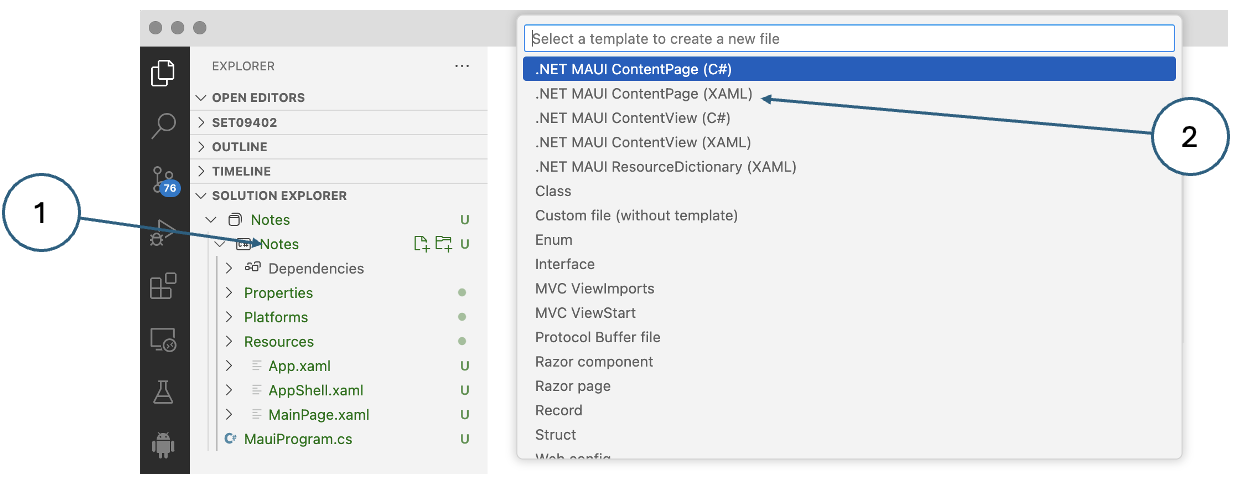
Select .NET MAUI ContentPage (XAML) and call the new page AboutPage.xaml. You do not have to type the extension - it will be added automatically.
- The AboutPage.xaml file will open a new document tab, displaying all of the XAML markup that represents the UI of the page. Replace the XAML markup with the following markup:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<ContentPage xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/dotnet/2021/maui"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
x:Class="Notes.AboutPage">
<VerticalStackLayout Spacing="10" Margin="10">
<HorizontalStackLayout Spacing="10">
<Image Source="dotnet_bot.png"
SemanticProperties.Description="The dot net bot waving hello!"
HeightRequest="64" />
<Label FontSize="22" FontAttributes="Bold" Text="Notes" VerticalOptions="End" />
<Label FontSize="22" Text="v1.0" VerticalOptions="End" />
</HorizontalStackLayout>
<Label Text="This app is written in XAML and C# with .NET MAUI." />
<Button Text="Learn more..." Clicked="LearnMore_Clicked" />
</VerticalStackLayout>
</ContentPage>
Let’s break down the key parts of the XAML controls placed on the page:
<ContentPage>is the root object for theAboutPageclass.<VerticalStackLayout>is the only child object of the ContentPage. ContentPage can only have one child object. The VerticalStackLayout type can have multiple children. This layout control arranges its children vertically, one after the other.<HorizontalStackLayout>operates the same as a<VerticalStackLayout>, except its children are arranged horizontally.<Image>displays an image, in this case it’s using thedotnet_bot.pngimage that comes with every .NET MAUI project.
Note
The file added to the project is actually
dotnet_bot.svg. .NET MAUI converts Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) files to Portable Network Graphic (PNG) files based on the target device. Therefore, when adding an SVG file to your .NET MAUI app project, it should be referenced from XAML or C# with a.pngextension. The only reference to the SVG file should be in your project file.
<Label>controls display text.<Button>controls can be pressed by the user, which raise theClickedevent. You can run code in response to theClickedevent.Clicked="LearnMore_Clicked"
The Clicked event of the button is assigned to the LearnMore_Clicked event
handler, which will be defined in the code-behind file. You’ll create this code
in the next step.
Handle the Clicked event
The next step is to add the code for the button’s Clicked event.
In the Solution Explorer pane of VSCode, expand the AboutPage.xaml file to reveal its code-behind file AboutPage.xaml.cs. Then click on the AboutPage.xaml.cs file to open it in the code editor.
Change the namespace to Notes instead of the default MauiApp1.
Add the following LearnMore_Clicked event handler code, which opens the
system browser to a specific URL:
1
2
3
4
5
private async void LearnMore_Clicked(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Navigate to the specified URL in the system browser.
await Launcher.Default.OpenAsync("https://aka.ms/maui");
}
Notice that the async keyword has been added to the method declaration,
which allows the use of the await keyword when opening the system browser.
Now that the XAML and code-behind of the AboutPage is complete, you’ll need
to get it displayed in the app.
Add image resources
Some controls can use images, which enhances how users interact with your app. In this section you’ll download two images, an About icon and a Notes icon in two formats, one for iOS and one for other platforms. The About icon will be used as a link to the page you created earlier, and the Notes icon will be used to navigate to a notes page that you will create in the next part of the tutorial.
iOS images:
Images for other plaforms:
After you’ve downloaded the images, you can move them with File Explorer or Finder to the Resources\Images folder of the project. Any file in this folder is automatically included in the project as a MauiImage resource.
Modify the app shell
As noted at the start of this article, the AppShell class defines an app’s
visual hierarchy, the XAML markup used in creating the UI of the app. Update
the XAML to add a TabBar control:
Click the AppShell.xaml file in the Solution Explorer pane to open the XAML editor. Replace the XAML markup with the following code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<Shell
x:Class="Notes.AppShell"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/dotnet/2021/maui"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:Notes"
Shell.FlyoutBehavior="Disabled">
<TabBar>
<ShellContent
Title="Notes"
ContentTemplate="{DataTemplate local:MainPage}"
Icon="{OnPlatform 'icon_notes.png', iOS='icon_notes_ios.png', MacCatalyst='icon_notes_ios.png'}" />
<ShellContent
Title="About"
ContentTemplate="{DataTemplate local:AboutPage}"
Icon="{OnPlatform 'icon_about.png', iOS='icon_about_ios.png', MacCatalyst='icon_about_ios.png'}" />
</TabBar>
</Shell>
Let’s break down the key parts of the XAML:
<Shell>is the root object of the XAML markup.<TabBar>is the content of the Shell.- Two
<ShellContent>objects inside of the<TabBar>. Before you replaced the template code, there was a single<ShellContent>object, pointing to theMainPagepage.
The TabBar and its children don’t represent any user interface elements,
but rather the organization of the app’s visual hierarchy. Shell takes these
objects and produces the user interface for the content, with a bar at the
top representing each page. The ShellContent.Icon property for each page
uses special syntax: {OnPlatform ...}. This syntax is processed when the
XAML pages are compiled for each platform, and with it you can specify a
property value for each platform. In this case, every platform uses the
icon_about.png icon by default, but iOS and MacCatalyst will use
icon_about_ios.png.
Each <ShellContent> object is pointing to a page to display. This is set
by the ContentTemplate property.
Run the app
With the emulator running, click the Run and Debug icon in the VSCode controls panel.
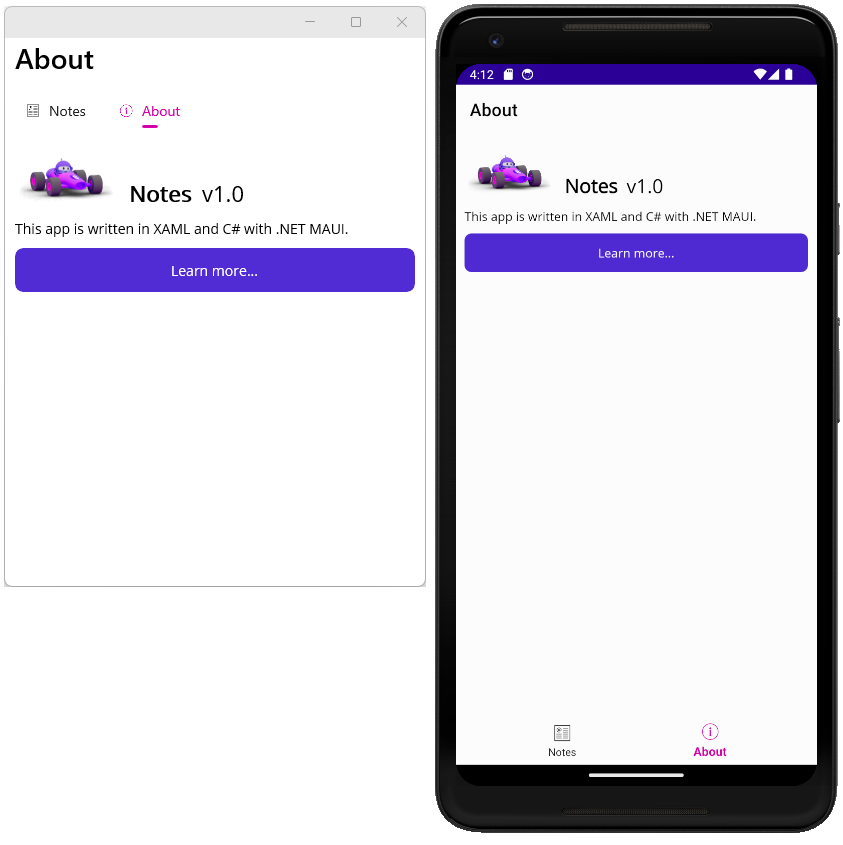
You’ll see that there are two tabs: Notes and About. Press the
About tab and the app navigates to the AboutPage you created. Press
on the Learn More… button to open the web browser.
3. Create a page for a note
Now that the app contains the MainPage and AboutPage, you can start
creating the rest of the app. First, you’ll create a page that allows a
user to create and display a note, and then you’ll write the code to load
and save the note.
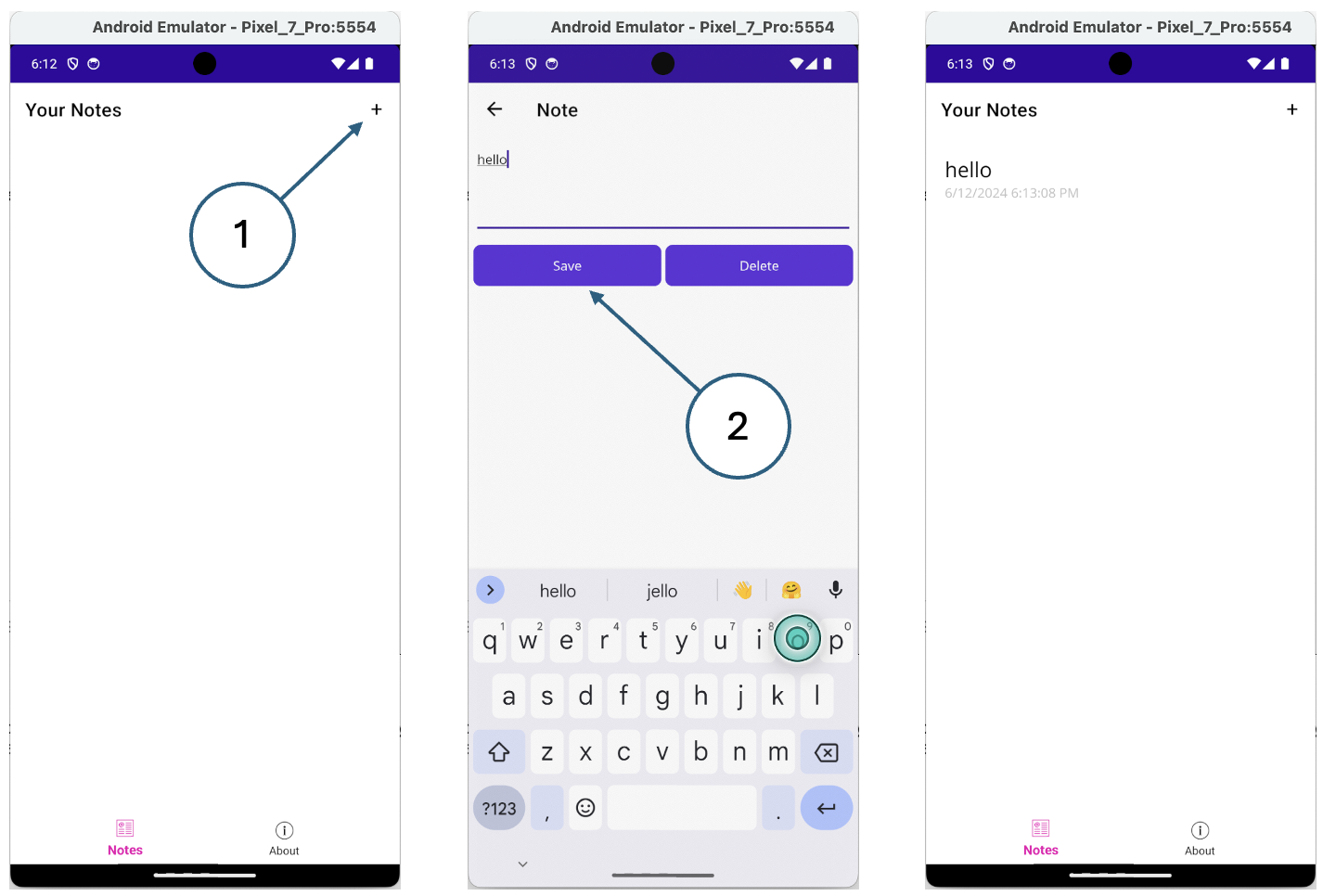
The note page will display the note and allow you to either save or delete it. First, add the new page to the project using the same procedure as you did in step 3. Name the new item NotePage.xaml.
The NotePage.xaml file will open in a new tab, displaying all of the XAML markup that represents the UI of the page. Replace the XAML code markup the following markup:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
<!--?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?-->
<ContentPage xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/dotnet/2021/maui"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
x:Class="Notes.NotePage"
Title="Note">
<VerticalStackLayout Spacing="10" Margin="5">
<Editor x:Name="TextEditor"
Placeholder="Enter your note"
HeightRequest="100" />
<Grid ColumnDefinitions="\*,\*" ColumnSpacing="4">
<Button Text="Save"
Clicked="SaveButton_Clicked" />
<Button Grid.Column="1"
Text="Delete"
Clicked="DeleteButton_Clicked" />
</Grid>
</VerticalStackLayout>
</ContentPage>
Let’s break down the key parts of the XAML controls placed on the page:
<VerticalStackLayout>arranges its children controls vertically, one below the other.<Editor>is a multi-line text editor control, and is the first control inside VerticalStackLayout<Grid>is a layout control, and is the second control inside of VerticalStackLayout
The Grid control defines columns and rows to create cells. Child controls are placed within those cells.
By default, the Grid control contains a single row and column,
creating a single cell. Columns are defined with a width, and the * value
for width tells the column to fill up as much space as possible. The previous
snippet defined two columns, both using as much space as possible, which
evenly distributes the columns in the allotted space: ColumnDefinitions="*,*".
The column sizes are separated by a , character.
Columns and rows defined by a Grid are indexed starting at 0. So the first column would be index 0, the second column is index 1, and so on.
Two <Button> controls are inside the <Grid> and assigned a column. If
a child control doesn’t define a column assignment, it’s automatically
assigned to the first column. In this markup, the first button is the “Save”
button and automatically assigned to the first column, column 0. The second
button is the “Delete” button and assigned to the second column, column 1.
Notice the two buttons have the Clicked event handled. You’ll add the
code for those handlers in the next section.
Load and save a note
Open the NotePage.xaml.cs code-behind file using the Solution Explorer to expand the NotePage.xaml entry, revealing the NotePage.xaml.cs file. Click the file to open it.
When you add a new XAML file, the code-behind contains a single line in the
constructor, a call to the InitializeComponent method:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
namespace Notes;
public partial class NotePage : ContentPage
{
public NotePage()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
}
The InitializeComponent method reads the XAML markup and initializes all
of the objects defined by the markup. The objects are connected in their
parent-child relationships, and the event handlers defined in code are
attached to events set in the XAML.
Now that you understand a little more about code-behind files, you’re going to add code to the NotePage.xaml.cs code-behind file to handle loading and saving notes.
-
When a note is created, it’s saved to the device as a text file. The name of the file is represented by the
_fileNamevariable. Add the followingstringvariable declaration to theNotePageclass:public partial class NotePage : ContentPage { string _fileName = Path.Combine(FileSystem.AppDataDirectory, “notes.txt”);
The code above constructs a path to the file, storing it in the app’s local data directory. The file name is notes.txt.
-
In the constructor of the class, after the
InitializeComponentmethod is called, read the file from the device and store its contents in theTextEditorcontrol’sTextproperty:1 2 3 4 5 6 7
public NotePage() { InitializeComponent(); if (File.Exists(_fileName)) TextEditor.Text = File.ReadAllText(_fileName); }
-
Next, add the code to handle the
Clickedevents defined in the XAML:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
private void SaveButton_Clicked(object sender, EventArgs e) { // Save the file. File.WriteAllText(_fileName, TextEditor.Text); } private void DeleteButton_Clicked(object sender, EventArgs e) { // Delete the file. if (File.Exists(_fileName)) File.Delete(_fileName); TextEditor.Text = string.Empty; }
The
SaveButton_Clickedmethod writes the text in the Editor control, to the file represented by the_fileNamevariable.The
DeleteButton_Clickedmethod first checks if the file represented by the_fileNamevariable, and if it exists, deletes it. Next, the Editor control’s text is cleared.
The final code for the code-behind file should look like the following:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
namespace Notes;
public partial class NotePage : ContentPage
{
string _fileName = Path.Combine(FileSystem.AppDataDirectory, "notes.txt");
public NotePage()
{
InitializeComponent();
if (File.Exists(_fileName))
TextEditor.Text = File.ReadAllText(_fileName);
}
private void SaveButton_Clicked(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Save the file.
File.WriteAllText(_fileName, TextEditor.Text);
}
private void DeleteButton_Clicked(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Delete the file.
if (File.Exists(_fileName))
File.Delete(_fileName);
TextEditor.Text = string.Empty;
}
}
Test the note
Now that note page is finished, you need a way to present it to the user.
Open the AppShell.xaml file, and change the first ShellContent
entry to point to the NotePage instead of MainPage:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<Shell
x:Class="Notes.AppShell"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/dotnet/2021/maui"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:Notes"
Shell.FlyoutBehavior="Disabled">
<TabBar>
<ShellContent
Title="Notes"
ContentTemplate="{DataTemplate local:NotePage}"
Icon="{OnPlatform 'icon_notes.png', iOS='icon_notes_ios.png', MacCatalyst='icon_notes_ios.png'}" />
<ShellContent
Title="About"
ContentTemplate="{DataTemplate local:AboutPage}"
Icon="{OnPlatform 'icon_about.png', iOS='icon_about_ios.png', MacCatalyst='icon_about_ios.png'}" />
</TabBar>
</Shell>
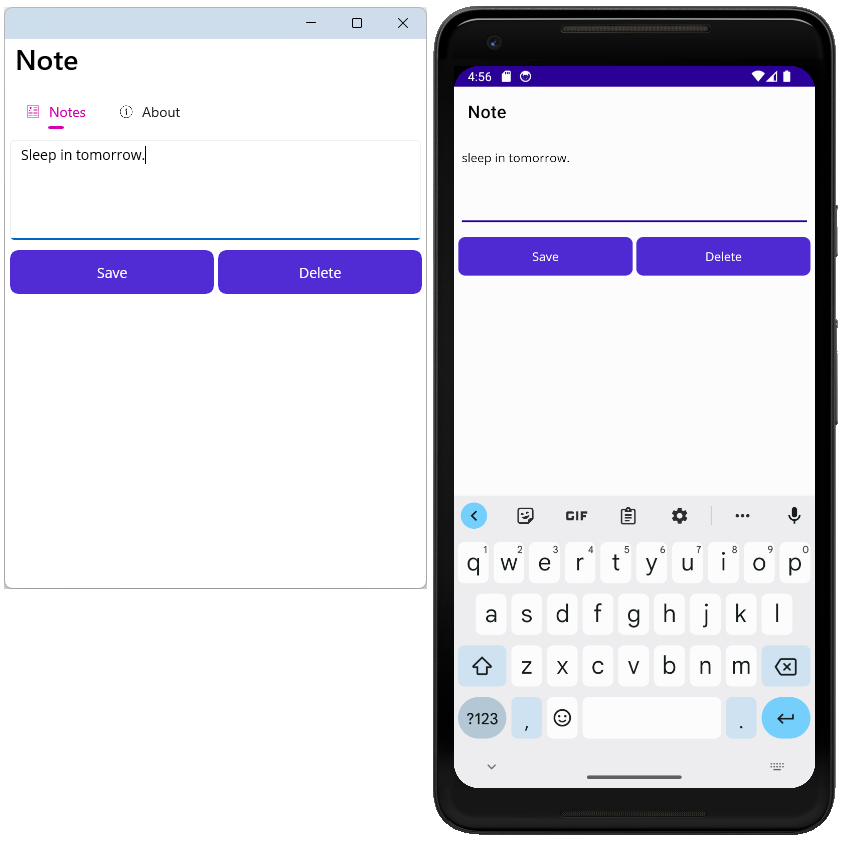
Save the file and run the app. Try typing into the entry box and press the Save button. Close the app, and reopen it. The note you entered should be loaded from the device’s storage.
4. Bind data to the UI and navigate pages
This portion of the tutorial introduces the concepts of views, models, and in-app navigation.
In the previous steps of the tutorial, you added two pages to the project:
NotePage and AboutPage. The pages represent a view of data. The NotePage
is a “view” that displays “note data” and the AboutPage is a “view” that
displays “app information data.” Both of these views have a model of that
data hardcoded, or embedded in them, and you’ll need to separate the data
model from the view.
What is the benefit of separating the model from the view? It allows you to design the view to represent and interact with any portion of the model without worrying about the actual code that implements the model. This is accomplished using data binding, something that will be presented later in this tutorial. For now, though, let’s restructure the project.
Separate the view and model
Refactor the existing code to separate the model from the view. The next few steps will organize the code so that views and models are defined separately from each other.
- Delete MainPage.xaml and MainPage.xaml.cs from your project, they’re no longer needed.
Tip
Deleting the MainPage.xaml item should also delete the MainPage.xaml.cs item too. If MainPage.xaml.cs wasn’t deleted, right-click on it and select Delete.
- Right-click on the Notes project and select Add > New Folder. Name the folder Models.
- Right-click on the Notes project and select Add > New Folder. Name the folder Views.
- Find the NotePage.xaml item and drag it to the Views folder. The NotePage.xaml.cs should move with it.
Tip
VSCode may not allow you to move items in the Solution Explorer by dragging and dropping. Instead, use the file browser pane at the top of the explorer panel. Here, you will have to move both the .xaml file and the .xaml.cs files separately.
- Find the AboutPage.xaml item and drag it to the Views folder. The AboutPage.xaml.cs should move with it.
Update the view namespace
Now that the views have been moved to the Views folder, you’ll need to update the
namespaces to match. The namespace for the XAML and code-behind files of the pages
is set to Notes. This needs to be updated to Notes.Views.
-
In the Solution Explorer pane, expand both NotePage.xaml and AboutPage.xaml to reveal the code-behind files:
Fig. 7. View files in VSCode. -
Double-click on the NotePage.xaml.cs item to open the code editor. Change the namespace to
Notes.Views:namespace Notes.Views;
- Repeat the previous steps for the AboutPage.xaml.cs item.
-
Double-click on the NotePage.xaml item to open the XAML editor. The old namespace is referenced through the
x:Classattribute, which defines which class type is the code-behind for the XAML. This entry isn’t just the namespace, but the namespace with the type. Change thex:Classvalue toNotes.Views.NotePage:1
x:Class="Notes.Views.NotePage"
- Repeat the previous step for the AboutPage.xaml item, but set the
x:Classvalue toNotes.Views.AboutPage.
Fix the namespace reference in Shell
The AppShell.xaml defines two tabs, one for the NotesPage and another for AboutPage. Now that those two pages were moved to a new namespace, the type mapping in the XAML is now invalid. In the Solution Explorer pane, double-click on the AppShell.xaml entry to open it in the XAML editor. It should look like the following snippet:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<Shell
x:Class="Notes.AppShell"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/dotnet/2021/maui"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:Notes"
Shell.FlyoutBehavior="Disabled">
<TabBar>
<ShellContent
Title="Notes"
ContentTemplate="{DataTemplate local:NotePage}"
Icon="{OnPlatform 'icon_notes.png', iOS='icon_notes_ios.png', MacCatalyst='icon_notes_ios.png'}" />
<ShellContent
Title="About"
ContentTemplate="{DataTemplate local:AboutPage}"
Icon="{OnPlatform 'icon_about.png', iOS='icon_about_ios.png', MacCatalyst='icon_about_ios.png'}" />
</TabBar>
</Shell>
A .NET namespace is imported into the XAML through an XML namespace declaration. In the
previous XAML markup, it’s the xmlns:local="clr-namespace:Notes" attribute in the root
element: <Shell>. The format of declaring an XML namespace to import a .NET namespace
in the same assembly is:
xmlns:{XML namespace name}=”clr-namespace:{.NET namespace}”
So the previous declaration maps the XML namespace of local to the .NET namespace of
Notes. It’s common practice to map the name local to the root namespace of your project.
Remove the local XML namespace and add a new one. This new XML namespace will map
to the .NET namespace of Notes.Views, so name it views. The declaration should
look like the following attribute: xmlns:views="clr-namespace:Notes.Views".
The local XML namespace was used by the ShellContent.ContentTemplate properties,
change them to views. Your XAML should now look like the following snippet:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<Shell
x:Class="Notes.AppShell"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/dotnet/2021/maui"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
xmlns:views="clr-namespace:Notes.Views"
Shell.FlyoutBehavior="Disabled">
<TabBar>
<ShellContent
Title="Notes"
ContentTemplate="{DataTemplate views:NotePage}"
Icon="{OnPlatform 'icon_notes.png', iOS='icon_notes_ios.png', MacCatalyst='icon_notes_ios.png'}" />
<ShellContent
Title="About"
ContentTemplate="{DataTemplate views:AboutPage}"
Icon="{OnPlatform 'icon_about.png', iOS='icon_about_ios.png', MacCatalyst='icon_about_ios.png'}" />
</TabBar>
</Shell>
You should now be able to run the app without any compiler errors, and everything should still work as before.
Define the model
Currently, the model is the data that is embedded in the note and about views. We’ll create new classes to represent that data. First, the model to represent a note page’s data:
-
In the Solution Explorer pane, right-click on the Models folder and select Add New File….
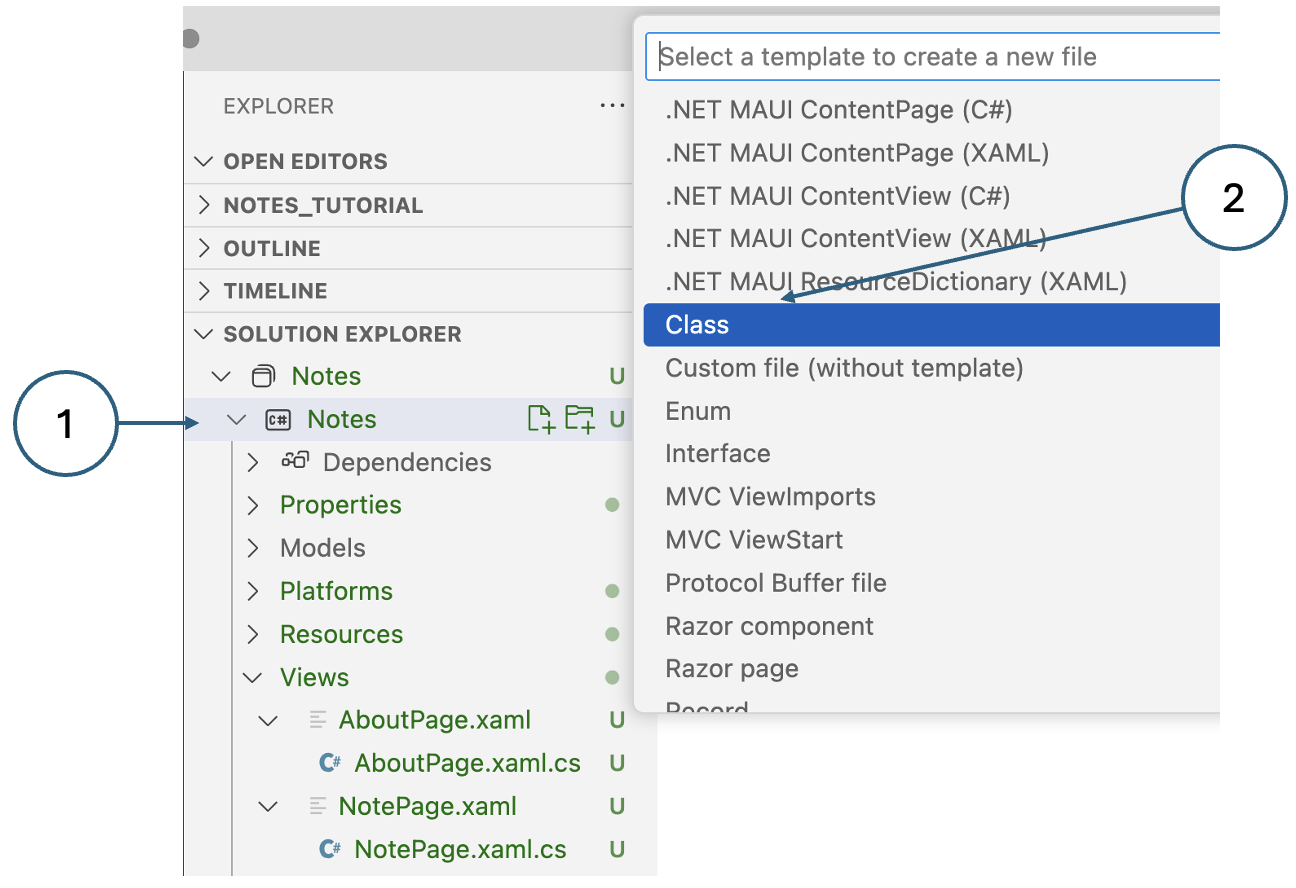
Fig. 8. Creating a new class in VSCode. - Name the class
Noteand press RETURN. Notice that VSCode will automatically add the .cs extension to the filename. -
Note.cs is opened automatically after creation. Replace the default content with the following snippet:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
namespace Notes.Models; internal class Note { public string? Filename { get; set; } public string? Text { get; set; } public DateTime? Date { get; set; } }
Information
The question marks after the datatypes in the code above indicate that these properties are all nullable. This is not necessarily what we want in the long run, but for now, this will allow us to run the app with no errors.
Next, create the about page’s model:
- In the Solution Explorer pane, right-click on the Models folder and select Add New File….
- Create a new class called
About. -
Replace the default content of the new file with the following snippet:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
namespace Notes.Models; internal class About { public string Title => AppInfo.Name; public string Version => AppInfo.VersionString; public string MoreInfoUrl => "https://aka.ms/maui"; public string Message => "This app is written in XAML and C# with .NET MAUI."; }
Update About page
The about page will be the quickest page to update and you’ll be able to run the app and see how it loads data from the model.
- In the Solution Explorer pane, open the Views/AboutPage.xaml file.
-
Replace the content with the following snippet:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?> <ContentPage xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/dotnet/2021/maui" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml" xmlns:models="clr-namespace:Notes.Models" x:Class="Notes.Views.AboutPage"> <ContentPage.BindingContext> <models:About /> </ContentPage.BindingContext> <VerticalStackLayout Spacing="10" Margin="10"> <HorizontalStackLayout Spacing="10"> <Image Source="dotnet_bot.png" SemanticProperties.Description="The dot net bot waving hello!" HeightRequest="64" /> <Label FontSize="22" FontAttributes="Bold" Text="{Binding Title}" VerticalOptions="End" /> <Label FontSize="22" Text="{Binding Version}" VerticalOptions="End" /> </HorizontalStackLayout> <Label Text="{Binding Message}" /> <Button Text="Learn more..." Clicked="LearnMore_Clicked" /> </VerticalStackLayout> </ContentPage>
Let’s look at the changes in the new snippet:
-
xmlns:models="clr-namespace:Notes.Models"This line maps the
Notes.Models.NET namespace to themodelsXML namespace. -
The
BindingContextproperty of the ContentPage is set to an instance of theNote.Models.Aboutclass, using the XML namespace and object ofmodels:About. This was set using property element syntax instead of an XML attribute.
Important!
Until now, properties have been set using an XML attribute. This works great for simple values, such as a
Label.FontSizeproperty. But if the property value is more complex, you must use property element syntax to create the object. Consider the following example of a creating a label with itsFontSizeproperty set:
The same FontSize property can be set using property element syntax:
-
Three
<Label>controls had theirTextproperty value changed from a hardcoded string to binding syntax:{Binding PATH}.{Binding}syntax is processed at run-time, allowing the value returned from the binding to be dynamic. ThePATHportion of{Binding PATH}is the property path to bind to. The property comes from the current control’sBindingContext. With the<Label>control,BindingContextis unset. Context is inherited from the parent when it’s unset by the control, which in this case, the parent object setting context is the root object: ContentPage.The object in the
BindingContextis an instance of theAboutmodel. The binding path of one of the labels binds theLabel.Textproperty to theAbout.Titleproperty.
The final change to the about page is updating the button click that opens a web page. The URL was hardcoded in the code-behind, but the URL should come from the model that is in the BindingContext property.
- In the Solution Explorer pane, open the Views/AboutPage.xaml.cs file.
-
Replace the
LearnMore_Clickedmethod with the following code:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
private async void LearnMore_Clicked(object sender, EventArgs e) { if (BindingContext is Models.About about) { // Navigate to the specified URL in the system browser. await Launcher.Default.OpenAsync(about.MoreInfoUrl); } }
The condition checks if the BindingContext is a Models.About type, and if it is,
assigns it to the about variable. The line inside the if statement opens the browser
to the URL provided by the about.MoreInfoUrl property.
Run the app and you should see that it runs exactly the same as before. Try changing the about model’s values and see how the UI and URL opened by the browser also change.
Update Note page
The previous section bound the about page view to the about model, and now you’ll do the same, binding the note view to the note model. However, in this case, the model won’t be created in XAML but will be provided in the code-behind in the next few steps.
- In the Solution Explorer pane, open the Views/NotePage.xaml file.
-
Change the
<Editor>control adding theTextproperty. Bind the property to theTextproperty:<Editor ... Text="{Binding Text}":1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?> <ContentPage xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/dotnet/2021/maui" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml" x:Class="Notes.Views.NotePage" Title="Note"> <VerticalStackLayout Spacing="10" Margin="5"> <Editor x:Name="TextEditor" Placeholder="Enter your note" Text="{Binding Text}" HeightRequest="100" /> <Grid ColumnDefinitions="\*,\*" ColumnSpacing="4"> <Button Text="Save" Clicked="SaveButton_Clicked" /> <Button Grid.Column="1" Text="Delete" Clicked="DeleteButton_Clicked" /> </Grid> </VerticalStackLayout> </ContentPage>
The modifications for the code-behind are more complicated than the XAML. The current
code is loading the file content in the constructor, and then setting it directly to
the TextEditor.Text property. Here is what the current code looks like:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
public NotePage()
{
InitializeComponent();
if (File.Exists(_fileName))
TextEditor.Text = File.ReadAllText(_fileName);
}
Instead of loading the note in the constructor, create a new LoadNote method. This
method will do the following:
- Accept a file name parameter.
- Create a new note model and set the file name.
- If the file exists, load its content into the model.
- If the file exists, update the model with the date the file was created.
- Set the
BindingContextof the page to the model.
- In the Solution Explorer pane, open the Views/NotePage.xaml.cs file.
-
Add the following method to the class:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
private void LoadNote(string fileName) { Models.Note noteModel = new Models.Note(); noteModel.Filename = fileName; if (File.Exists(fileName)) { noteModel.Date = File.GetCreationTime(fileName); noteModel.Text = File.ReadAllText(fileName); } BindingContext = noteModel; }
-
Update the class constructor to call
LoadNote. The file name for the note should be a randomly generated name to be created in the app’s local data directory.1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
public NotePage() { InitializeComponent(); string appDataPath = FileSystem.AppDataDirectory; string randomFileName = $"{Path.GetRandomFileName()}.notes.txt"; LoadNote(Path.Combine(appDataPath, randomFileName)); }
5. Add a view and model that lists all notes
This portion of the tutorial adds the final piece of the app, a view that displays all of the notes previously created.
Multiple notes and navigation
Currently the note view displays a single note. To display multiple notes, create a
new view and model: AllNotes.
- In the Solution Explorer pane, right-click on the Views folder and select Add New File….
- Select the .NET MAUI ContentPage (XAML) template. Name the file AllNotesPage.xaml, and press RETURN.
- In the Solution Explorer pane, right-click on the Models folder and select Add New File…
- Create a new class called AllNotes.cs.
Code the AllNotes model
The new model will represent the data required to display multiple notes. This data
will be a property that represents a collection of notes. The collection will be an
ObservableCollection which is a specialized collection. When a control which lists
multiple items, such as a ListView, is bound to an ObservableCollection,
the two work together to automatically keep the list of items in sync with the
collection. If the list adds an item, the collection is updated. If the collection
adds an item, the control is automatically updated with a new item.
- In the Solution Explorer pane, open the Models/AllNotes.cs file.
-
Replace the code with the following snippet:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
using System.Collections.ObjectModel; namespace Notes.Models; internal class AllNotes { public ObservableCollection<Note> Notes { get; set; } = new ObservableCollection<Note>(); public AllNotes() => LoadNotes(); public void LoadNotes() { Notes.Clear(); // Get the folder where the notes are stored. string appDataPath = FileSystem.AppDataDirectory; // Use Linq extensions to load the \*.notes.txt files. IEnumerable<Note> notes = Directory // Select the file names from the directory .EnumerateFiles(appDataPath, "\*.notes.txt") // Each file name is used to create a new Note .Select(filename => new Note() { Filename = filename, Text = File.ReadAllText(filename), Date = File.GetLastWriteTime(filename) }) // With the final collection of notes, order them by date .OrderBy(note => note.Date); // Add each note into the ObservableCollection foreach (Note note in notes) Notes.Add(note); } }
The previous code declares a collection, named Notes, and uses the LoadNotes
method to load notes from the device. This method uses LINQ extensions to
load, transform, and sort the data into the Notes collection.
Design the AllNotes page
Next, the view needs to be designed to support the AllNotes model.
- In the Solution Explorer pane, open the Views/AllNotesPage.xaml> file.
-
Replace the code with the following markup:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?> <ContentPage xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/dotnet/2021/maui" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml" x:Class="Notes.Views.AllNotesPage" Title="Your Notes"> <!-- Add an item to the toolbar --> <ContentPage.ToolbarItems> <ToolbarItem Text="Add" Clicked="Add_Clicked" IconImageSource="{FontImage Glyph='+', Color=Black, Size=22}" /> </ContentPage.ToolbarItems> <!-- Display notes in a list --> <CollectionView x:Name="notesCollection" ItemsSource="{Binding Notes}" Margin="20" SelectionMode="Single" SelectionChanged="notesCollection_SelectionChanged"> <!-- Designate how the collection of items are laid out --> <CollectionView.ItemsLayout> <LinearItemsLayout Orientation="Vertical" ItemSpacing="10" /> </CollectionView.ItemsLayout> <!-- Define the appearance of each item in the list --> <CollectionView.ItemTemplate> <DataTemplate> <StackLayout> <Label Text="{Binding Text}" FontSize="22"/> <Label Text="{Binding Date}" FontSize="14" TextColor="Silver"/> </StackLayout> </DataTemplate> </CollectionView.ItemTemplate> </CollectionView> </ContentPage>
The previous XAML introduces a few new concepts:
-
The
ContentPage.ToolbarItemsproperty contains aToolbarItem. The buttons defined here are usually displayed at the top of the app, along the page title. Depending on the platform, though, it may be in a different position. When one of these buttons is pressed, theClickedevent is raised, just like a normal button.The
ToolbarItem.IconImageSourceproperty sets the icon to display on the button. The icon can be any image resource defined by the project, however, in this example, aFontImageis used. AFontImagecan use a single glyph from a font as an image. -
The
CollectionViewcontrol displays a collection of items, and in this case, is bound to the model’sNotesproperty. The way each item is presented by the collection view is set through theCollectionView.ItemsLayoutandCollectionView.ItemTemplateproperties.For each item in the collection, the
CollectionView.ItemTemplategenerates the declared XAML. TheBindingContextof that XAML becomes the collection item itself, in this case, each individual note. The template for the note uses two labels, which are bound to the note’sTextandDateproperties. -
The
CollectionViewhandles theSelectionChangedevent, which is raised when an item in the collection view is selected.
The code-behind for the view needs to be written to load the notes and handle the events.
- In the Solution Explorer pane, open the Views/AllNotesPage.xaml.cs file.
-
Replace the code with the following snippet:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36
namespace Notes.Views; public partial class AllNotesPage : ContentPage { public AllNotesPage() { InitializeComponent(); BindingContext = new Models.AllNotes(); } protected override void OnAppearing() { ((Models.AllNotes)BindingContext).LoadNotes(); } private async void Add_Clicked(object sender, EventArgs e) { await Shell.Current.GoToAsync(nameof(NotePage)); } private async void notesCollection_SelectionChanged(object sender, SelectionChangedEventArgs e) { if (e.CurrentSelection.Count != 0) { // Get the note model var note = (Models.Note)e.CurrentSelection\[0\]; // Should navigate to "NotePage?ItemId=path\\on\\device\\XYZ.notes.txt" await Shell.Current.GoToAsync($"{nameof(NotePage)}?{nameof(NotePage.ItemId)}={note.Filename}"); // Unselect the UI notesCollection.SelectedItem = null; } } }
This code uses the constructor to set the BindingContext of the page to the model.
The OnAppearing method is overridden from the base class. This method is automatically
called whenever the page is shown, such as when the page is navigated to. The code here
tells the model to load the notes. Because the CollectionView in
the AllNotes view is bound to the AllNotes model’s Notes property, which is an
ObservableCollection, whenever the notes are loaded, the
CollectionView is automatically updated.
The Add_Clicked handler introduces another new concept, navigation. Because the app
is using .NET MAUI Shell, you can navigate to pages by calling the
Shell.Current.GoToAsync method. Notice that the handler is declared with the async
keyword, which allows the use of the await keyword when navigating. This handler
navigates to the NotePage.
The last piece of code in the previous snippet is the notesCollection_SelectionChanged
handler. This method takes the currently selected item, a Note model, and uses its
information to navigate to the NotePage. GoToAsync uses a URI
string for navigation. In this case, a string is constructed that uses a query string
parameter to set a property on the destination page. The interpolated string
representing the URI ends up looking similar to the following string:
NotePage?ItemId=path\on\device\XYZ.notes.txt
The ItemId= parameter is set to the file name on the device where the note is stored.
Note
VSCode may be indicating that the NotePage.ItemId property doesn’t exist, which it
doesn’t. The next step is modifying the Note view to load the model based on the
ItemId parameter that you’ll create.
Query string parameters
The Note view needs to support the query string parameter, ItemId. Create it now:
- In the Solution Explorer pane, open the Views/NotePage.xaml.cs file.
-
Add a new string property named
ItemId. This property calls theLoadNotemethod, passing the value of the property, which in turn, should be the file name of the note:1 2 3 4
public string ItemId { set { LoadNote(value); } }
-
Add the
QueryPropertyattribute to theclasskeyword, providing the name of the query string property, and the class property it maps to,ItemIdandItemIdrespectively:1 2
\[QueryProperty(nameof(ItemId), nameof(ItemId))\] public partial class NotePage : ContentPage
-
Replace the
SaveButton_ClickedandDeleteButton_Clickedhandlers with the following code:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
private async void SaveButton_Clicked(object sender, EventArgs e) { if (BindingContext is Models.Note note) File.WriteAllText(note.Filename, TextEditor.Text); await Shell.Current.GoToAsync(".."); } private async void DeleteButton_Clicked(object sender, EventArgs e) { if (BindingContext is Models.Note note) { // Delete the file. if (File.Exists(note.Filename)) File.Delete(note.Filename); } await Shell.Current.GoToAsync(".."); }
The buttons are now
async. After they’re pressed, the page navigates back to the previous page by using a URI of.. - Delete the
_fileNamevariable from the top of the code, as it’s no longer used by the class.
Modify the app’s visual tree
The AppShell is still loading the single note page, instead, it needs to load the
AllPages view. Open the AppShell.xaml file and change the first ShellContent
entry to point to the AllNotesPage instead of NotePage:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<Shell
x:Class="Notes.AppShell"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/dotnet/2021/maui"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
xmlns:views="clr-namespace:Notes.Views"
Shell.FlyoutBehavior="Disabled">
<TabBar>
<ShellContent
Title="Notes"
ContentTemplate="{DataTemplate views:AllNotesPage}"
Icon="{OnPlatform 'icon_notes.png', iOS='icon_notes_ios.png', MacCatalyst='icon_notes_ios.png'}" />
<ShellContent
Title="About"
ContentTemplate="{DataTemplate views:AboutPage}"
Icon="{OnPlatform 'icon_about.png', iOS='icon_about_ios.png', MacCatalyst='icon_about_ios.png'}" />
</TabBar>
</Shell>
If you run the app now, you’ll notice it crashes if you press the Add button,
complaining that it can’t navigate to NotesPage. Every page that can be navigated
to from another page, needs to be registered with the navigation system. The
AllNotesPage and AboutPage pages are automatically registered with the navigation
system by being declared in the TabBar.
Register the NotesPage with the navigation system:
- In the Solution Explorer pane, open the App.xaml.cs file.
-
Add a line to the constructor that registers the navigation route:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
namespace Notes; public partial class AppShell : Shell { public AppShell() { InitializeComponent(); Routing.RegisterRoute(nameof(Views.NotePage), typeof(Views.NotePage)); MainPage = new AppShell(); } }
The Routing.RegisterRoute method takes two parameters:
- The first parameter is the string name of the URI you want to register, in this case
the resolved name is
"NotePage". - The second parameter is the type of page to load when
"NotePage"is navigated to.
Now you can run your app. Try adding new notes, navigating back and forth between notes, and deleting notes.